
In business and marketing, the terms “marketing funnel” and “sales funnel” are frequently used interchangeably; they each fulfill distinct roles in converting potential customers into actual buyers. Particular purposes and have different stages, strategies, and metrics. Understanding the differences between these funnels is crucial for any business aiming to optimize its marketing and sales efforts. In this extensive guide, we will delve into the depths of the marketing and sales funnel separately, highlighting their objectives, stages, strategies, and metrics.
By the end of this article, you will clearly understand the marketing funnel vs sales funnel and how these funnels work and complement each other in driving success.
What Is A Marketing Funnel?
The marketing funnel is a strategic framework businesses employ to lead potential customers through a sequence of stages, ultimately leading them to brand awareness and interest in their products or services. Its primary objective is to foster awareness and generate leads for the business.
Stages Of The Marketing Funnel
The marketing funnel concept holds a pivotal role in sales and marketing that outlines the potential progression of the customer’s journey, starting from the initial awareness phase and culminating in eventual conversion. Here’s a more details of each stage:
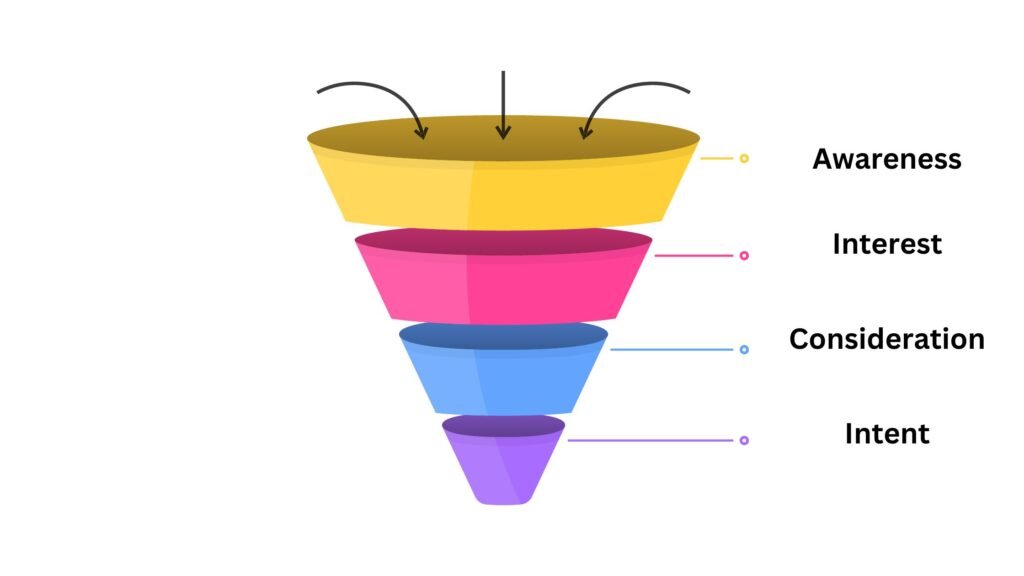
Awareness:
- Content Creation: This involves producing high-quality, informative content that addresses the challenges or concerns of your target audience’s interests or questions. This can be in the form of blog posts, articles, videos, infographics, or podcasts. The objective is to generate content that draws in and educates potential customers.
- Social Media Engagement involves actively interacting with your audience on various social media platforms. Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn can help you reach a wider audience. Share your content, interact with comments and messages, and Utilize pertinent hashtags to enhance your brand’s visibility.
- Influencer Marketing: includes forming partnerships with influencers within your industry and leveraging their established audiences. Influencers can create content or endorse your product, exposing it to their followers and potentially increasing brand awareness.
Interest:
- Email Marketing: It entails gathering email addresses from prospects who have expressed interest through sign-up forms or lead magnets on your website. Then, nurture these leads with targeted emails that provide valuable content, showcase your expertise, and gradually build trust.
- Webinars: Host webinars or online workshops that delve Delve more profoundly into subjects associated with your product or industry. Webinars offer an exceptional means to connect with your audience effectively in real-time, answer questions, and establish your brand as a knowledgeable authority.
- Downloadable Resources: Offer valuable resources such as ebooks, whitepapers, templates, or checklists in exchange for contact information. These resources can provide in-depth information and further demonstrate your expertise.
Consideration:
- Product Demos: Allow potential customers to see your product or service. Whether through live demonstrations, video tutorials, or interactive simulations, this helps them understand how your offering can solve their specific problems.
- Customer Testimonials: Share real-life success stories and testimonials from satisfied customers. These provide social proof and build trust by showing how others have benefited from your product or service.
- Interactive Content: quizzes, calculators, or surveys that engage and educate your audience. Interactive Utilizing content enjoyably and efficiently can help prospects evaluate their needs and the value of your offering.
Intent:
- Abandoned Cart Emails: For e-commerce businesses, when a potential customer leaves their shopping cart without completing a purchase, send automated follow-up emails. These emails often include reminders. For items remaining in the cart, businesses may provide incentives, such as discounts or free shipping, to motivate conversion.
- Limited-Time Offers: Create a feeling of urgency by presenting limited-time offers, time-limited promotions, or discounts. This tactic can motivate potential customers to take advantage of the offer quickly.
- Personalized Recommendations: Use data and user behavior to provide personalized product or content recommendations. Tailoring your suggestions to a customer’s interests and preferences can increase the likelihood of conversion.
What Is A Sales Funnel?
The sales funnel, on the other hand, is designed to guide leads through becoming paying customers. Its primary purpose is to close deals and generate revenue.
Stages Of The Sales Funnel
The sales funnel focuses on the stages that lead to converting potential customers into paying customers. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of each stage:
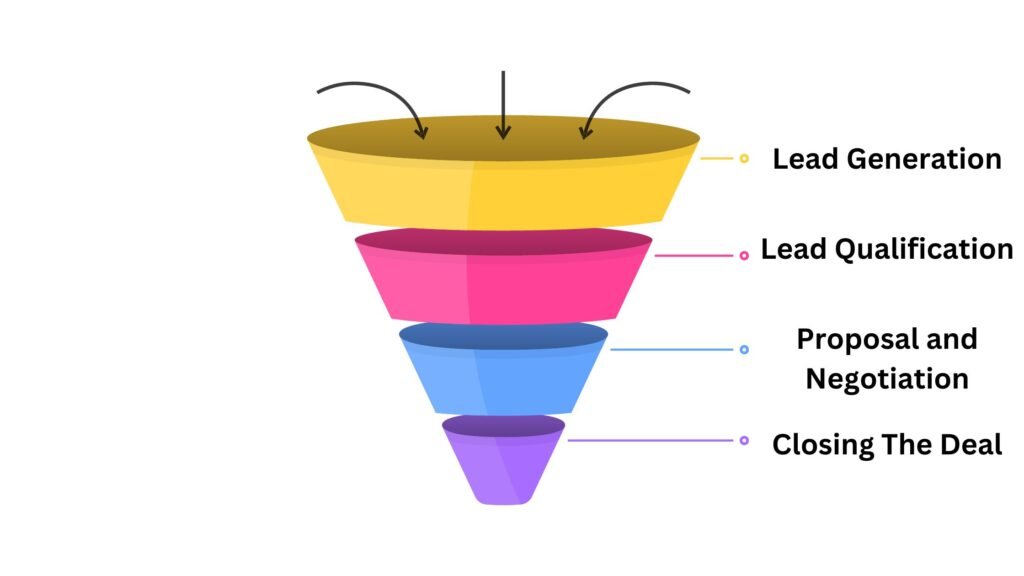
Lead Generation:
- In this initial stage, potential customers enter the sales funnel. These prospects might come from various sources, including marketing-qualified leads (MQLs) generated by marketing efforts and outbound prospecting activities.
- Lead generation strategies include content marketing, social media advertising, email marketing, and alternative approaches to attract potential customers.
Lead Qualification:
- Leads are assessed and evaluated in this stage to determine their interest and fit for the product or service. The goal is to identify which leads have the potential to become customers.
- Leads are often categorized as sales-qualified leads (SQLs) or disqualified based on their level of engagement, budget, authority, need, and timeline (commonly known as BANT criteria).
Proposal and Negotiation:
- Once a lead is qualified as an SQL, sales representatives engage with them to understand their specific needs, present proposals, and negotiate terms.
- This stage involves addressing any objections or concerns the lead may have and working toward a mutually agreeable solution.
- Sales presentations, product demos, and pricing and customization discussions often occur during this stage.
Closing The Deal:
- The final stage of the sales funnel is where leads are converted into paying customers.
- This may involve various actions such as contract signing, payment processing, and the initiation of onboarding processes to ensure a smooth transition from prospect to customer.
- Successful closure of the deal is the ultimate goal of the sales funnel.
Marketing Funnel Vs Sales Funnel: What’s The Differences
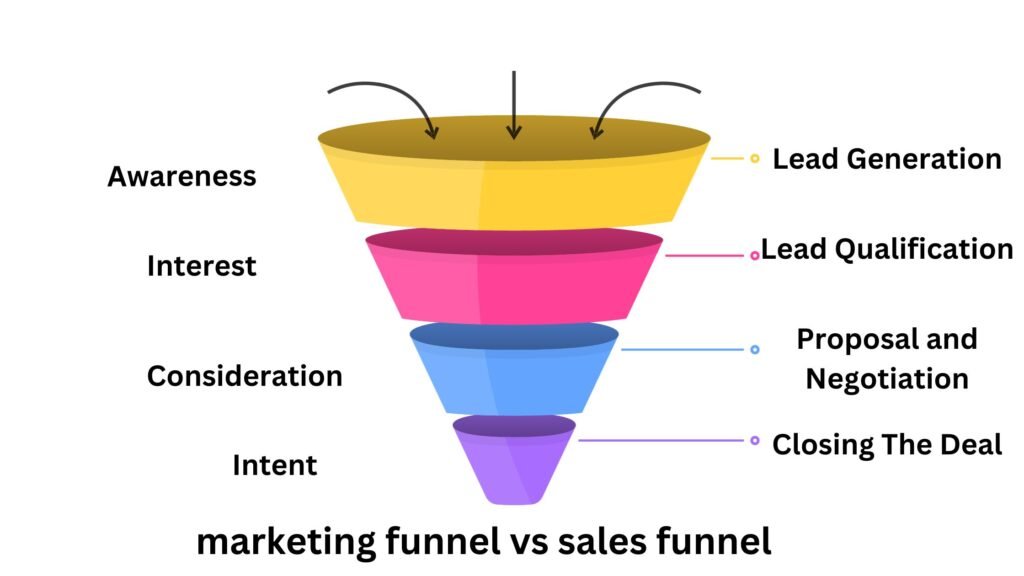
While interconnected concepts, marketing, and sales funnels fulfill distinct purposes and concentrate on separate customer journey stages. Here are the key differences between the two:
Purpose
- Marketing Funnel: The primary objective of a marketing funnel is to draw in and captivate potential customers, leading them through a structured journey from initial awareness to cultivating interest and consideration for a particular product or service. This involves building brand awareness, creating interest by showcasing the value proposition and generating leads through various marketing strategies. The marketing funnel systematically guides prospects through different stages, laying the groundwork for a potential conversion.
- Sales Funnel: In contrast, the primary goal of a sales funnel is to convert leads into actual customers or prospects into paying clients. The sales funnel focuses on the critical stages of lead qualification, presenting proposals, engaging in negotiations, and closing deals. It is a strategic process designed to efficiently move potential customers from the awareness and consideration stages to the final decision-making phase, where they become paying customers. The sales funnel is instrumental in optimizing the sales process and maximizing the chances of successful conversions by addressing potential clients’ specific needs and concerns.
Focus
- Marketing Funnel: The marketing funnel focuses on the top-of-the-funnel (TOFU) and middle-of-the-funnel (MOFU) stages. At the top, the emphasis is on creating awareness through targeted content creation and advertising. In the middle, the goal is to nurture leads and generate interest, often involving lead-generation strategies to move potential customers closer to conversion.
- Sales Funnel: Sales funnels concentrate on the middle-of-the-funnel (MOFU) and bottom-of-the-funnel (BOFU) stages. The middle stage involves lead qualification, where potential customers are assessed for conversion likelihood. The bottom stage is dedicated to sales presentations, negotiation, and the crucial step of closing deals. The sales funnel focuses on progressing leads through these stages to achieve successful conversions.
Activities
- Marketing Funnel: Activities within a marketing funnel encompass various strategies to create awareness and interest. Content marketing, social media engagement, advertising campaigns, search engine optimization (SEO), and other similar approaches are employed. The goal is to attract potential customers, generate interest in the product or service, and initiate the lead generation process.
- Sales Funnel: Sales funnel activities involve more direct interactions with leads. This includes conducting sales calls, delivering presentations to showcase the value proposition, creating proposals tailored to the potential customer’s needs, engaging in negotiation, finalizing contracts, and processing payments. The sales funnel’s activities target converting qualified leads into paying customers through personalized and targeted interactions.
Key Metrics
- Marketing Funnel: Key metrics in a marketing funnel revolve around gauging the effectiveness of top-of-the-funnel (TOFU) and middle-of-the-funnel (MOFU) activities. That includes monitoring website traffic to assess visibility, click-through rates to evaluate engagement, conversion rates to measure the transition from interest to leads, and various engagement metrics on social media platforms, such as likes, shares, and comments.
- Sales Funnel: In the sales funnel, key metrics are tailored to evaluate the progression of leads through the stages and the ultimate conversion into paying customers. Metrics include conversion rates at each stage, providing insights into the efficiency of the funnel. Sales velocity measures how quickly deals move through the funnel, while average deal size indicates revenue potential. Win/loss rates provide feedback on the effectiveness of sales strategies, and overall revenue generated is a crucial indicator of success in the sales funnel.
Handoff
- Marketing Funnel: In the marketing funnel, the handoff involves passing marketing-qualified leads (MQLs) to the sales team. These leads have shown interest and engagement with the marketing efforts but may need further nurturing and qualification before they are ready for direct sales engagement. The marketing-to-sales handoff is a crucial transition point to ensure a smooth and informed transition of leads from marketing efforts to the sales process.
- Sales Funnel: In the sales funnel, the process takes over once leads have been qualified as sales-qualified leads (SQLs) through activities such as lead scoring. The focus shifts to converting these qualified leads into actual customers. That involves more direct sales interactions, including presentations, negotiations, and closing deals. The handoff from marketing to sales ensures the leads are well-prepared and more likely to convert into paying customers.
Goal
- Marketing Funnel: The primary goal of a marketing funnel is to cultivate interest and generate leads. The marketing funnel expands awareness and attracts potential customers by employing strategies like content marketing, social media engagement, and advertising. It focuses on building a sizable pool of leads to be nurtured and eventually handed off to the sales team for further qualification and conversion.
- Sales Funnel: In contrast, the main objective of a sales funnel is to convert leads into paying customers, thereby contributing directly to the business’s revenue. Through stages like lead qualification, sales presentations, negotiations, and deal closure, the sales funnel guides prospects from their initial interest to purchase. The ultimate goal is to maximize conversions and drive financial success for the business.
What Strategies Bridge The Gap Between The Sales Funnel and the Marketing Funnel?

Several strategies and tactics can be employed to bridge the gap between the marketing funnel and sales funnel and ensure a smooth transition of leads from marketing to sales. Here are key strategies:
- Lead Scoring: Introduce a lead scoring system that allocates values to leads based on their level of engagement and fits with the ideal customer profile. Marketing can pass leads to sales when they reach a specific score, indicating they are sales-ready.
- Lead Nurturing: Establish a lead nurturing program where marketing continues to engage with leads in the consideration stage. This helps keep leads warm and educates them until they are ready to purchase.
- Marketing Automation: Use marketing automation platforms to track lead behavior and trigger personalized follow-up messages. These platforms can also automate lead handoffs to sales when specific criteria are met.
- Sales and Marketing Alignment: Foster strong collaboration and communication between the sales and marketing teams. Regular meetings and shared goals help both teams understand each other’s challenges and objectives.
- CRM Integration: Ensure seamless integration between the customer relationship management (CRM) system used by sales and marketing automation tools. This integration allows for efficient lead transfer and tracking.
- Content Mapping: Align marketing content with the different stages of the buyer’s journey. Marketing materials should address both early-stage awareness needs and later-stage decision-making requirements.
- Closed-Loop Reporting: Establish a feedback loop where sales provide insights on lead quality and conversion rates. Marketing can then refine their strategies based on this feedback.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Create SLAs between marketing and sales teams, specifying expectations for lead follow-up times and how leads are handled. This ensures accountability and a smooth handoff process.
- Lead Qualification Criteria: Precisely outline the criteria for a “sales-qualified lead” (SQL). This ensures that marketing and sales understand when to Determine the point at which a lead is prepared for handoff to the sales team.
- Sales Enablement: Provide sales teams with the tools and resources to engage with leads effectively. This includes training, sales collateral, and access to customer data collected by marketing.
FAQs
Q1. What Role Does Content Marketing Play In The Marketing Funnel?
It holds a crucial role in the marketing funnel. It provides valuable and relevant content to engage and educate potential customers at different stages Throughout their journey, spanning awareness, consideration, and decision-making phases. It helps build brand awareness, establish credibility, nurture leads, and drive conversions by addressing prospects’ specific needs and questions along the way.
Q2. How Can I Optimize My Sales Funnel For Higher Conversion Rates?
To enhance the conversion rates of your sales funnel, optimize focus on segmentation, personalization, and streamlining the sales process. Segment your leads to tailor messaging, personalize interactions to meet individual needs, and simplify the process to reduce friction. Implement lead nurturing, use social proof, track and analyze data, provide clear calls to action, train your sales team continuously, gather feedback, automate repetitive tasks, and optimize landing pages. These steps will help drive more conversions and improve your overall sales funnel performance.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions and interplay between the marketing and sales funnel is pivotal for any business aiming to maximize its revenue potential. The marketing funnel primarily focuses on building awareness and interest among potential customers, while the sales funnel takes the baton to convert those prospects into paying customers.
What are your thoughts on the marketing funnel vs. sales funnel debate? Have you encountered unique challenges or devised innovative solutions in your business? Feel free to share your insights in the comments below, and let’s continue this discussion.








No Comments