
In the ever-evolving marketing world, where the landscape is saturated with messages and choices, one strategy stands out as a beacon of innovation and effectiveness: micro-marketing. It’s a term buzzing through the corridors of marketing departments and boardrooms and for a good reason. Micromarketing is not just a buzzword; it’s a paradigm shift in how businesses approach their customers.
In this blog, we will extensively explore the concept of micro marketing, discussing its definition, significance, the various types it encompasses, and its pros and cons. We will also provide real-world examples to illustrate how micro-marketing works and conclude with a summary.
So, let’s get started;
What Is Micro Marketing?
Micromarketing is a targeted marketing strategy that targets specific individuals or niche market segments with highly personalized and tailored marketing messages, products, or services.
Unlike traditional mass marketing, which aims to reach a broad and general audience, micromarketing zooms in on a much narrower and well-defined subset of potential customers.
Importance Of Micro Marketing
- Personalization: One of the primary reasons for the importance of micromarketing is personalization. In today’s highly competitive marketplace, consumers expect personalized experiences. Micromarketing allows businesses to tailor their offerings, messages, and interactions to meet individual customers’ unique needs and preferences. This fosters stronger customer relationships and loyalty.
- Efficiency: Micromarketing optimizes resource allocation. By targeting specific segments or individuals likely to convert, businesses can reduce wasteful spending on marketing efforts that may not reach their intended audience. That results in a more efficient allocation of resources, leading to better ROI.
- Higher Conversion Rates: When marketing messages are highly relevant and tailored, they are more likely to resonate with the target audience. This, in turn, increases conversion rates. Micromarketing strategies aim to create a stronger emotional connection with customers, making them more inclined to take the desired action, whether purchasing, signing up for a newsletter, or engaging with content.
- Competitive Advantage: Micromarketing allows businesses to gain a competitive edge. When a company can effectively serve the unique needs of a specific market segment, it becomes challenging for competitors to replicate the same level of personalization and customer satisfaction.
- Data-Driven Insights: Micromarketing relies heavily on data analysis. Businesses gather valuable insights about customer behavior, preferences, and trends. These insights can inform product development, pricing strategies, and future marketing campaigns, helping companies stay ahead of market changes.
- Customer Retention: Micro marketing strategies foster customer loyalty by continuously analyzing and responding to individual customer needs. Loyal customers are more likely to make repeat purchases and become brand advocates, contributing to long-term business success.
Now that you know what micro marketing is and why it’s important, let’s delve into the various types of micro marketing.
Types Of Micromarketing
Loyalty-Based Micromarketing
Loyalty-based micromarketing focuses on nurturing and rewarding existing customers who have demonstrated loyalty to a brand. It aims to maintain and strengthen the relationship with these customers by offering them personalized incentives, discounts, exclusive offers, or loyalty rewards. This type of micromarketing acknowledges and appreciates the value of long-term customer relationships.
Local-Based Micromarketing
Local-based micromarketing targets customers within specific geographic locations. It tailors marketing efforts to address the local population’s unique preferences, needs, and cultural aspects. This approach recognizes that consumer behaviors and tastes can vary significantly from region to region, and businesses aim to connect with local audiences on a more personal level.
Relationship-Based Micromarketing
Relationship-based micromarketing emphasizes building and nurturing individual relationships with customers. It goes beyond transactions to create emotional connections and trust. Businesses engage in personalized communication, remembering past interactions, and demonstrating genuine interest in customers’ well-being to foster long-term loyalty and advocacy.
Industry-Based Micromarketing
Industry-based micromarketing segments customers according to the industries they work in or the associated sectors. It acknowledges that different industries may have unique challenges, regulations, or trends. By understanding industry-specific nuances, businesses can provide solutions and content that resonate with their target customers in those industries.
Customer-Based Micromarketing
Customer-based micromarketing takes a deep dive into individual customer profiles. It analyzes customer data, behaviors, preferences, and purchase histories to create highly customized marketing messages and offerings. Businesses aim to provide a one-to-one marketing experience, delivering content and products tailored to each customer’s unique characteristics.
Customer Recovery Micromarketing
Customer recovery micromarketing focuses on winning back customers who may have had a negative experience or have become inactive. It aims to re-engage these customers by addressing their concerns or grievances, offering incentives, and delivering personalized messages demonstrating the company’s commitment to resolving issues and providing a better experience.
Each type of micro-marketing strategy caters to specific objectives and audience segments, allowing businesses to engage with customers on a highly personalized level. By understanding these segments’ distinct characteristics and needs, companies can craft more relevant and effective marketing campaigns, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction, retention, and overall business success.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Micromarketing
Advantages Of Micromarketing

- Improved Customer Engagement: Micromarketing fosters deeper customer engagement by providing relevant and meaningful interactions. Customers are more likely to engage with content and offer catering to their interests and needs.
- Higher ROI: Targeting specific segments or individuals reduces wasted marketing spend. That leads to a higher return on investment as marketing resources are directed toward those most likely to convert.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Customers feel valued and understood When they receive personalized experiences and offers. That enhances overall customer satisfaction and can lead to positive word-of-mouth referrals.
- Better Data Utilization: Micromarketing relies on data-driven insights. That encourages businesses to systematically collect and analyze customer data, leading to a better understanding of customer behavior and preferences.
- Competitive Advantage: Micromarketing can create a competitive advantage by delivering superior customer experiences that are difficult for competitors to replicate.
- Adaptability: Micromarketing strategies can be adjusted and refined quickly in response to changing market conditions, ensuring businesses remain agile and responsive.
Disadvantages Of Micromarketing
- Data Privacy Concerns: The extensive collection and use of customer data raise privacy concerns. Companies must navigate complex regulations and ensure customer data is handled ethically and securely.
- Resource Intensive: Effective micromarketing requires substantial resources, including data analysis tools, skilled personnel, and marketing technology investments. Small businesses with limited budgets may need help to implement advanced micromarketing strategies.
- Complexity: Managing multiple micromarketing campaigns for various customer segments can become complex and resource-intensive. It may require significant organizational effort and coordination.
- Risk of Overpersonalization: While personalization is a strength of micromarketing, there is a risk of overpersonalization. Bombarding customers with overly customized content can be perceived as intrusive or creepy.
- Limited Reach: By focusing narrowly on specific segments or individuals, businesses may miss out on potential customers who don’t fit neatly into predefined categories.
By now, you’ve gained a comprehensive understanding of micro marketing. If you’re wondering about its effectiveness, here are two illustrative examples that showcase how it can yield tangible results.
Examples Of Micro Marketing
- Coca-Cola Launched A “Share A Coke” Marketing Campaign

Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” campaign started in Australia and became a big hit. They did something unique – they printed popular names on Coke bottles and encouraged people to share these personalized bottles with their friends and family. This campaign is an excellent example of micromarketing because it allowed Coca-Cola to connect with people in specific areas using popular names.
The results were impressive: in the first summer it ran in Australia, Coca-Cola sold over 250 million bottles with names on them, even though Australia has only around 23 million people. It showed how tailoring marketing to local preferences and individual names could be incredibly successful.
- L’Oreal Malaysia Uses Locally Created And User-Generated Content To Its Advantage
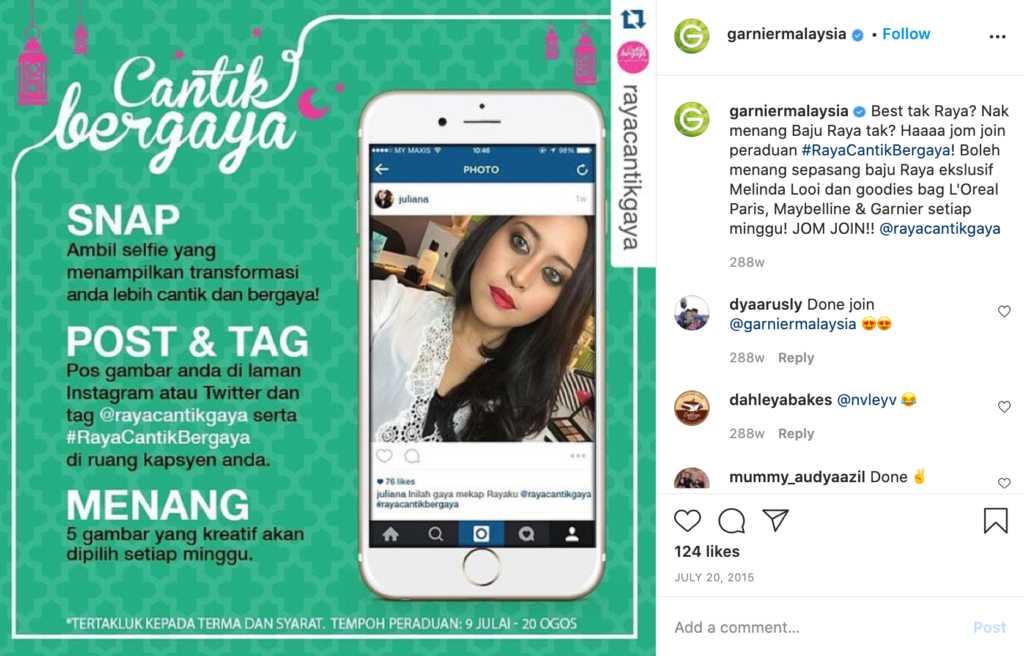
L’Oreal Malaysia found a clever way to reach more people in different places. They used regular people who have small but dedicated groups of followers (called micro-influencers) to talk about their products. These influencers made videos about L’Oreal, Maybelline, and Garnier products and shared them with their followers. This strategy worked well – L’Oreal Malaysia got more people interested in their products, with a 12.9% increase in engagement rates, and 1.9 million people saw the videos.
Instead of trying to make content that fits every place and culture, L’Oreal let local influencers do it for them, which worked great.
Conclusion
Now that you understand micromarketing consider implementing this strategy in your business to boost revenue. Take action today and observe its positive impact on your business’s growth and profitability.
If you have any questions about this marketing method, please leave them in the comment section. We will be happy to answer you.
Thanks for reading 🙂








No Comments