
Maintaining a competitive edge in the dynamic business realm necessitates employing a strategic marketing approach. This is where marketing frameworks come into play.
In this blog, we will delve into the importance of marketing frameworks and explore various types. Whether you have extensive experience in marketing or are new to the field, understanding and utilising marketing frameworks can significantly enhance your marketing success.
Let’s begin by gaining an understanding of what marketing frameworks entail.
What Are Marketing Frameworks?
Marketing frameworks are structured models or strategies designed to streamline and enhance a business’s marketing efforts. They provide a systematic approach to developing, implementing, and analysing marketing activities, ensuring that every step is aligned with the company’s overall objectives.
These frameworks help marketers organise their thoughts, plan strategically, and execute campaigns more effectively. By offering a clear roadmap, marketing frameworks enable businesses to understand their market, target the appropriate audience, and evaluate their endeavours’ effectiveness. Let’s explore their significance.
Importance Of Using Marketing Frameworks

- Structured Planning and Execution: It provides a structured approach to planning and executing marketing strategies. This setup ensures that every aspect of the marketing plan is considered, from identifying the target audience to crafting the message and selecting the appropriate channels. By following a systematic process, businesses can avoid common pitfalls and ensure a cohesive and comprehensive marketing strategy.
- Improved Focus and Direction: Using a marketing framework helps businesses maintain a clear focus on their goals. It guarantees that all marketing endeavours harmonise with the broader business goals, preventing the team from getting sidetracked by irrelevant trends or opportunities. This synchronisation improves the effectiveness of marketing endeavours and boosts the probability of attaining desired results.
- Enhanced Communication and Collaboration: Frameworks facilitate better communication and collaboration among team members by providing a common language and understanding. This shared understanding helps coordinate efforts, share insights, and make well-informed decisions, resulting in increased effectiveness and unified marketing campaigns.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: This approach often incorporates tools and methodologies for collecting and analysing data. It enables businesses to base decisions on factual evidence rather than intuition or guesswork. By continuously monitoring performance and adjusting strategies based on data insights, companies can optimise their marketing efforts for better results.
- Consistent Evaluation and Improvement: A key component of most marketing frameworks is continuous evaluation and improvement. Frameworks provide metrics and benchmarks for assessing the success of marketing activities. By regularly reviewing these metrics, businesses can identify areas for improvement, adapt their strategies, and ensure continuous growth and development.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: Marketing frameworks offer a versatile strategy that can be adjusted to various situations and changing market conditions. Whether a business is launching a new product, entering a new market, or responding to competitive pressures, a well-chosen framework provides the flexibility to adjust strategies accordingly. This adaptability ensures that marketing efforts remain relevant and effective in a dynamic business environment.
Now, let’s delve into the different kinds of frameworks.
Types Of Marketing Frameworks
AIDA (Attention, Interest, Desire, Action)
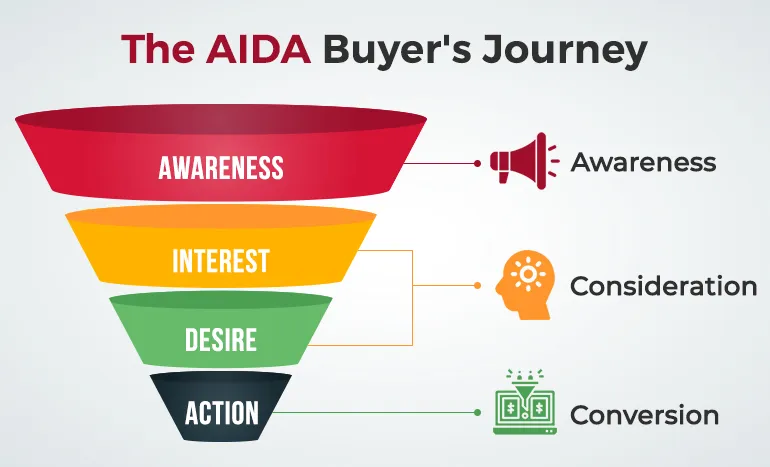
The AIDA framework guides marketers in capturing attention, building interest, creating desire, and prompting action from potential customers. Following these steps, businesses can craft compelling marketing campaigns that drive conversions. Let’s now dive into the framework:
- Attention: The first step in the AIDA framework is capturing the audience’s attention. This is done through eye-catching headlines, visuals, or unique propositions that make potential customers stop and take notice. Effective attention-grabbing techniques can include bold advertisements, intriguing social media posts, or engaging content.
- Interest: Once you have the audience’s attention, the next step is to build their interest. This involves providing relevant and valuable information. Highlighting the benefits of a product or service, sharing testimonials, or providing helpful content can keep the audience interested and engaged.
- Desire: After generating interest, the goal is to create a passion for the product or service. This is achieved by appealing to the audience’s emotions and showing them how the product can solve their problems or enhance their lives. Persuasive language, showcasing features, and offering incentives can build this desire.
- Action: The final step is encouraging the audience to promote action, whether purchasing, subscribing to a newsletter, or reaching out to the company. Clear calls-to-action (CTAs) and easy navigation on websites or apps help convert interest into tangible actions.
7Ps Of Marketing

The 7Ps framework encompasses all aspects of marketing, from developing products and setting prices to choosing distribution channels, promotions, people, processes, and physical evidence. It provides a holistic view of marketing strategies and helps businesses create comprehensive and effective marketing plans. Let’s now dive into it:
- Product refers to what the business offers, including goods or services. Understanding the product’s features, benefits, and unique selling points is crucial. Businesses need to ensure their product meets the needs and wants of their target market.
- Price: This involves determining the right pricing strategy. Factors like production costs, competitor pricing, and perceived value should be considered. The goal is to set a price that maximises profit while remaining attractive to customers.
- Place: This is about where and how the product is sold. It includes distribution channels, locations, and methods of delivery. Businesses must ensure their product is available where their target customers can easily access it.
- Promotion: Promotion covers how a business can communicate with and engage with its target audience to increase awareness and encourage purchases. This can include advertising, social media marketing, public relations, and sales promotions.
- People: This element focuses on everyone involved in the product or service, from employees to customers. Ensuring that staff are well-trained and customer-focused can significantly impact customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- The process involves the procedures and systems for delivering the product or service to the customer. Efficient and effective processes ensure that customers receive consistent, high-quality experiences.
- Physical Evidence: It refers to the tangible aspects that customers see and experience, which help to form their perceptions of the business. This can include branding, packaging, the physical environment of a store, or even website design.
STP Framework
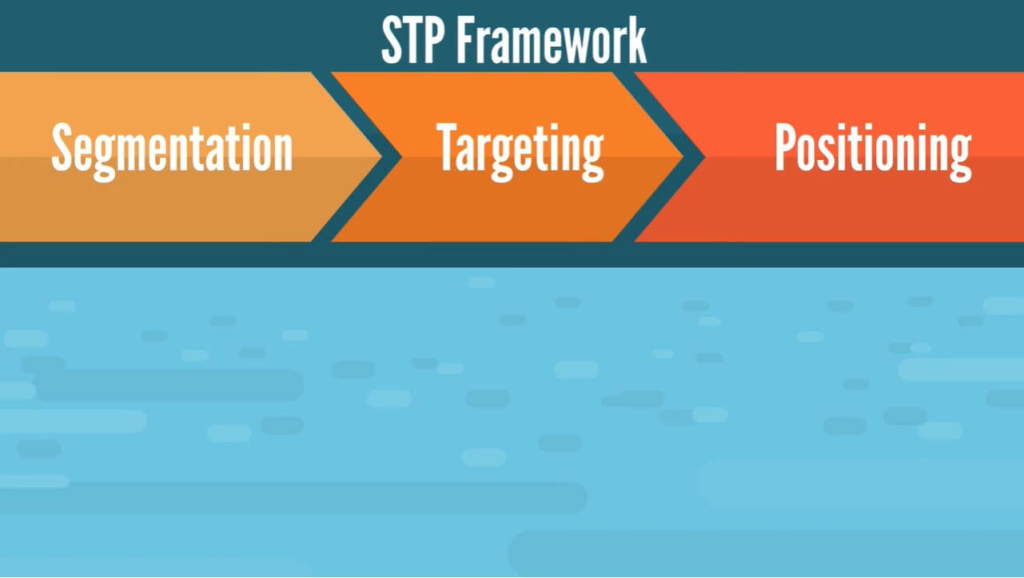
STP is a fundamental framework that divides the market, focuses on particular customer segments, and effectively positions products or services to meet those segments’ needs. It allows businesses to customise their marketing endeavours for maximum impact and relevance. Let’s now understand it in detail:
- Segmentation: Segmentation involves dividing the broader market into smaller, distinct groups of consumers who have similar needs, characteristics, or behaviours. This can be based on demographics, psychographics, geographic location, or behavioural patterns. The goal is to identify specific segments more likely to respond to marketing efforts.
- Targeting: After identifying market segments, the next step is targeting, which involves selecting the segments the business will focus on. This decision is based on segment size, profitability, and the company’s ability to serve these segments effectively. Businesses may choose one or multiple segments to target with tailored marketing strategies.
- Positioning: Positioning is about creating a unique and favourable image of the product or service in the target audience’s minds. It includes distinguishing the product from competitors and communicating its benefits and value proposition. Effective positioning helps establish a strong brand identity and fosters customer loyalty.
SWOT Analysis Framework
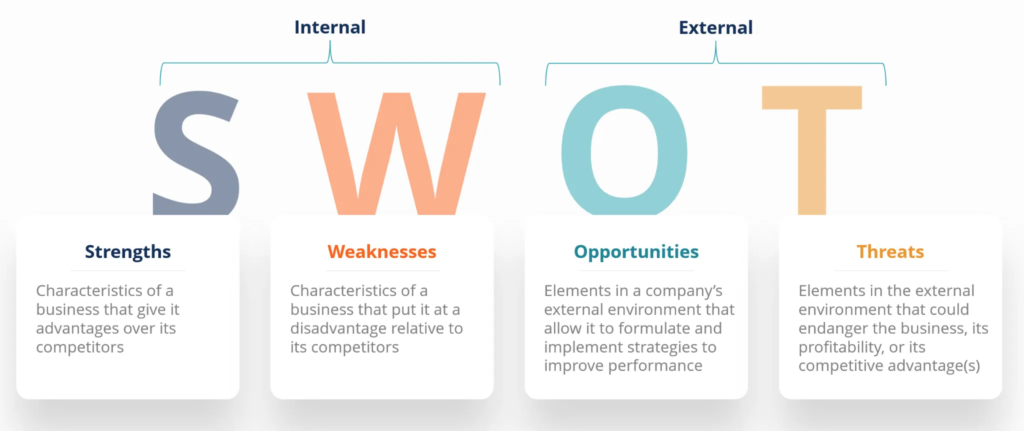
SWOT analysis is a strategic framework that assists businesses in identifying internal strengths and weaknesses as well as external opportunities and threats. It offers a systematic approach to strategic planning, allowing companies to capitalise on strengths, address weaknesses, exploit opportunities, and mitigate threats. Let’s now dive into the framework.
- Strengths: These internal factors give a business an advantage over its competitors. This can include a strong brand reputation, loyal customer base, unique technology, or skilled workforce. Identifying strengths helps companies to leverage them to achieve their goals.
- Weaknesses: These are internal factors that disadvantage a business. These include the need for more resources, better location, strong brand recognition, or operational inefficiencies. Recognising weaknesses is crucial for addressing and mitigating them.
- Opportunities: Opportunities are external factors a business can capitalise on to grow or improve its position. These might be market trends, changes in consumer behaviour, technological advancements, or gaps in the market. Identifying opportunities helps businesses to take proactive steps to exploit them.
- Threats: These are external factors that could cause trouble for the business. This could be new competitors, regulation changes, economic downturns, or shifts in consumer preferences. Identifying threats allows firms to develop strategies to protect against them.
Blue Ocean Strategy
The Blue Ocean Strategy framework encourages businesses to seek uncontested market spaces by creating new demand and offering unique value propositions. It focuses on value innovation, strategic moves, and redefining market boundaries for sustained growth and competitiveness. Let’s now dive into the framework.
- Uncontested Market Space: The Blue Ocean Strategy focuses on creating new, uncontested market spaces where competition is irrelevant. Instead of competing in overcrowded markets (red oceans), businesses aim to tap into new demand and offer unique value propositions. This involves innovating and thinking outside traditional market boundaries.
- Value Innovation: The Blue Ocean Strategy’s core concept is value innovation. This means simultaneously pursuing differentiation and low cost to open up a new market and create new demand. By offering unprecedented value at a lower price, businesses can attract a wider audience and make the competition irrelevant.
- Strategic Moves: Implementing a Blue Ocean Strategy requires a series of strategic moves that shift the focus from competing to creating. These moves involve redefining market boundaries, concentrating on the broader perspective, expanding beyond current demand, and aligning the strategic sequence correctly. Tools such as the Strategy Canvas and the Four Actions Framework (eliminate, reduce, raise, and create) help businesses visualise and plan their strategic moves effectively.
Content Marketing Funnel
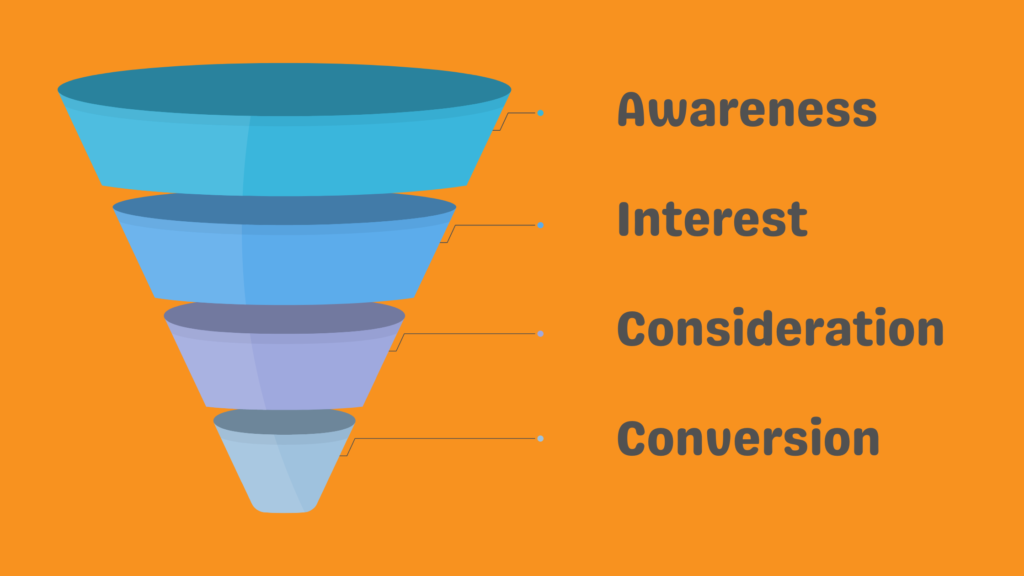
The Content Marketing Funnel maps the customer journey from awareness to conversion, leveraging valuable content at each stage to guide potential customers towards making purchasing decisions. It emphasises the importance of tailored content, engagement, and nurturing relationships for effective marketing outcomes. Let’s now dive into the framework.
- Awareness: Customers first become aware of a brand, product, or service in the awareness stage. They may have a problem or need they are trying to address. The goal of content at this stage is to attract the attention of potential customers and make them aware of your brand’s existence and what you offer. Types of content like blog posts, social media updates, infographics, and videos can effectively create awareness. The key is to provide valuable information that addresses the customer’s pain points or interests, positioning your brand as a relevant solution provider.
- Interest: Customers who know your brand move into the interest stage. Here, they start showing more interest in learning about your products or services. The content at this stage should focus on capturing the audience’s interest and offering more in-depth information about your offerings. This can include case studies, product demonstrations, white papers, and webinars. The goal is to spark the interest of potential customers and motivate them to delve deeper.
- Consideration: In the consideration stage, potential customers determine if your product or service meets their needs. Content at this stage should provide in-depth insights, comparisons with competitors, customer testimonials, and FAQs to address any doubts or questions they may have. The aim is to position your brand as a credible and trustworthy choice, guiding customers towards a favourable decision.
- Conversion: The final stage of the content marketing funnel is conversion, where potential customers decide to purchase from your brand. Content at this stage can include special offers, promotions, free trials, or product demos to incentivise conversions. The goal is to make the buying process seamless and appealing, encouraging customers to take action and complete the purchase. Post-conversion content such as thank-you emails, onboarding guides, and follow-up communications can also help nurture customer relationships and encourage repeat purchases or referrals.
By understanding and applying these marketing frameworks, businesses can develop more effective marketing strategies, better reach their target audience, and attain sustainable growth. Each framework offers unique insights and approaches, making it valuable in a marketer’s toolkit.
Now that you understand the various frameworks, let’s delve into the future of marketing frameworks.
Future Trends In Marketing Frameworks
Emerging Marketing Frameworks and Innovations: As the marketing landscape evolves, we expect to see new frameworks and innovative approaches emerging. These frameworks may focus on AI-powered marketing automation, predictive analytics for personalised marketing, and sustainability-driven frameworks that align with environmental and social values. These innovations address evolving consumer preferences, market dynamics, and technological advancements, providing businesses with fresh strategies to connect with their audience effectively.
The Role of Technology and Data Analytics: Advances in Technology and data analytics will remain essential and pivotal in shaping future marketing frameworks. AI and machine learning algorithms will facilitate greater accuracy in audience segmentation, real-time personalisation, and automated campaign optimisation. Advanced data analytics tools will empower businesses by extracting actionable insights from extensive data sets, resulting in informed decision-making and precise marketing tactics.
Predictions for the Future of Marketing Frameworks: Looking ahead, marketing frameworks are likely to become even more agile, adaptive, and customer-centric. We can anticipate integrating diverse data sources, such as IoT devices and social media sentiment analysis, to enhance customer understanding and engagement. Cross-channel integration and omnichannel marketing frameworks will become standard, providing seamless experiences across digital and physical touchpoints. Moreover, sustainability and ethical considerations will influence the development of frameworks that prioritise responsible marketing practices and community engagement.
Staying Ahead With Evolving Frameworks
Continuous Learning And Adaptation
Businesses can stay ahead by fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptation. Staying updated on industry trends, exploring novel frameworks, and embracing a growth mindset will enable organisations to evolve alongside changing market dynamics.
Collaboration And Innovation
Collaboration with industry peers, technology partners, and marketing experts can offer valuable insights and access to state-of-the-art tools and strategies. Embracing innovation and experimenting with emerging frameworks will allow businesses to stay agile, responsive, and competitive in a rapidly evolving marketing landscape.
Conclusion
Harnessing the power of marketing frameworks can be the key to business success. With a well-defined framework in place, you can effectively navigate the intricacies of the market, ensuring that your team is in sync and dedicated to the right strategies. Implementing a marketing framework today lays the foundation for a smoother journey tomorrow.
It’s not just about staying the course; it’s about thriving and reaching your goals more effectively. Create a marketing framework tailored to your business, and watch as it simplifies decision-making, keeps everyone informed, and drives your business towards more significant achievements.
However, if you still have any questions related to the blog, please feel free to leave them in the comment section below. We will be happy to answer them.
Thanks for reading 🙂








No Comments